Warts are benign (unlike malignant - no cancerous) skin formations, formed under the influence of various representatives of the human papillomavirus (HPV) family. ), of which there are more than a hundred. There is no gender or age barrier for warts: their prevalence is the same in both sexes and does not depend on age.
How are warts spread and what causes warts?
Papillomavirus is transmitted by contact: direct contact with a carrier (handshake), or through contaminated household items and the environment (in the bath, shower, swimming pool, etc. ). But don't shy away from the handshake of a colleague or good friend: infectious conditions are an unfavorable combination of several factors:
- Skin cracks and minor scratches, chronic abrasions. Risk group - those who, by the nature of their occupational activities, involve wet cleaning or hand washing: they have a lot of bacteria on their skin;
- weak immunity (indicator - frequent colds);
- sweaty hands and feet a lot.
If things don't go as planned, the first warts will appear after 1. 5 to 6 months: this is the incubation period of an infection caused by the HPV virus.
Types and symptoms of warts
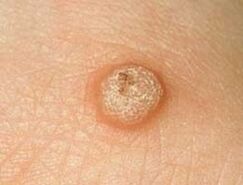
Common warts (also called vulgar warts)
Such warts account for two-thirds of all skin warts. In the same way, these warts are characterized by a recognizable age: they often appear in children and young schoolchildren.
Preferred locations for warts are the hands (both palms and back), fingers, and sometimes the face (which is very uncomfortable cosmetically). The appearance of a coarse wart is modest: a round nodule, ranging in size from the tip of a pin to a small pea. The color does not stand out on the skin. Single warts are rare: usually a few or all scattered. Moreover, one of the largest warts, it is called the mother wart. If you remove it, then the rest will go down on its own.
Flat warts (juvenile)
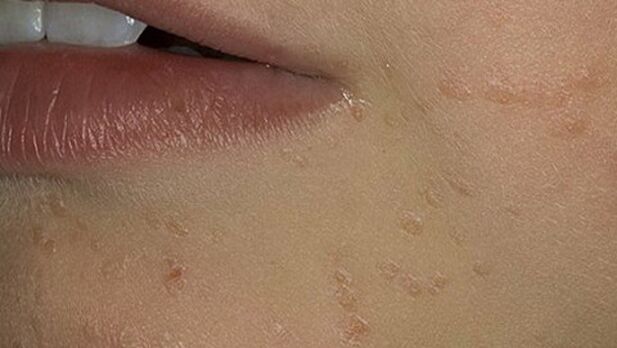
Another representative of "young" warts affects people from 10 to 25 years old. They are small flat papules, only slightly raised above the surface of the skin, with a smooth (sometimes scaly) surface. Flesh color, sometimes slightly yellow. Typically, flat warts are found on the backs of the hands, wrists, face, and neck. Sometimes - on the tip of the penis.
wart
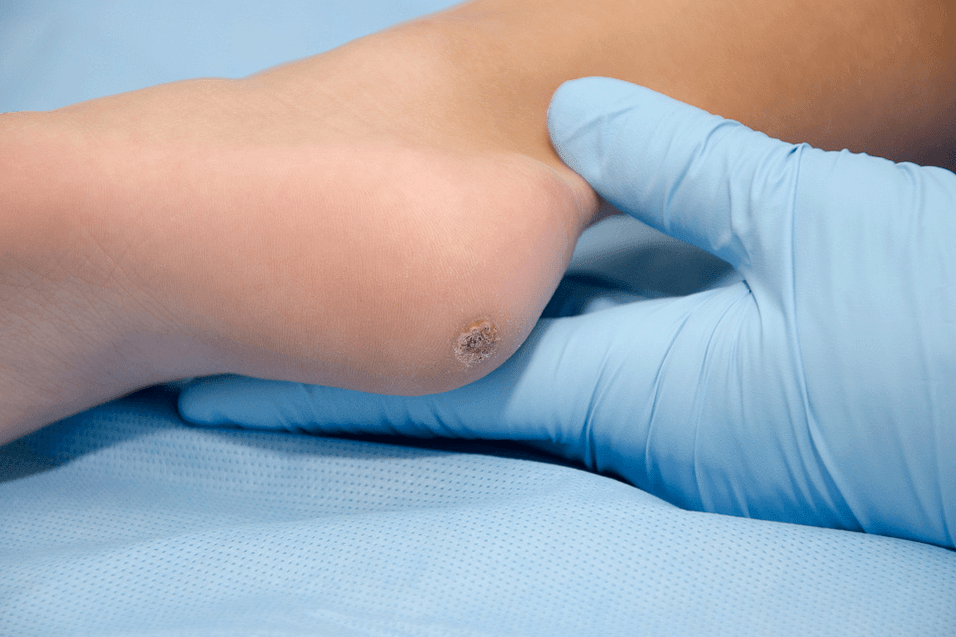
These warts are distinguished by increased pain sensation, especially felt when walking. Visually, warts are difficult to distinguish from calluses. They can be convex or concave. Plantar warts are raised in accordance with their name - on the soles of the feet, in the places of greatest friction.
Warts in old age (seborrhea)
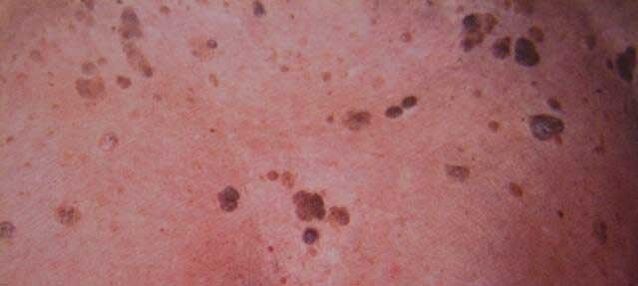
A benign epithelial tumor that forms over many years that occurs in old age is called senile wart. Initially just a small brown dot, over time growing, up to 5-6 cm in diameter, old acne (also known as seborrheic keratosis) has an oily and scaly surface. Over time, it thickens, its surface becomes covered with cracks and literally fills with dark brown. Aged warts form on intimate areas of the body, but they sometimes irritate their unwitting owners on the face, neck, and limbs.
Condylomas (genital warts)
These warts have a specific area: the genitals, the perineum, the vaginal opening, and the anus. They can appear in the armpits, under the female breasts, and in children - in the nasolabial folds. In appearance, they are often compared to honeycomb or cauliflower due to their segmented structure. The color of the warts is fleshy or pale pink, but if you rub them, they will turn crimson and start to bleed. They form large colonies.
Diagnosis of warts
Diagnosing warts isn't difficult, this isn't rocket technology for you. Just look at the clinical manifestations of these undesirable developments. Plant warts are distinguished from calluses by their former papillae, genital warts with broad warts, which are indicative of secondary syphilis, by their denser consistency, wide base, and moist surface.
Wart treatment
Warts are removed by medical or mechanical means. Given their viral "nature", they are fought accordingly: antiviral ointments are prescribed. This will prevent the wart from spreading to undeveloped areas. Among folk methods, the milky decoction of celandine, which stands out on the cut of the plant, has gained popularity.
Electrocautery (current exposure + high temperature) helps to remove warts even in the most severe cases.
Cryotherapy (cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen) is very suitable for treating vulvar warts. This procedure is practically painless, so it is convenient to use in children.
Plantar warts are treated in a complex way: first - by cold aspiration, then - surgically, removing the affected tissue area under local anesthesia.
Laser therapy is also used, using different types of rays. The affected area depends on this to evaporate or solidify.
Usually there are no particular problems with warts, but recurrences do occur. And in about half of the cases, they go away on their own without any treatment.
As a precautionary measure, it can be advised to promptly respond to the appearance of even a single wart and immediately take measures to eliminate it.

























