
Labia papillomas are pathogenic structures in the female genital area caused by one or more genotypes of the papilloma virus. And although not all strains that stimulate tumor growth in this area cause cancer, the disease must be treated. Even small growths in such a sensitive area can get damaged and subsequently cause a number of complications. Considering how common this disease is, every woman should know what to do about papillomas of the labia, which doctor to consult and what procedures to perform. Special attention should be paid to preventive measures, because practically no one can avoid papillomas on the labia minora.
Causes of papillomas on the labia

Having seen images of papillomas on the labia, one should not blame the patient for being promiscuous. Indeed, HPV is often transmitted through intimate intimacy, but this is not the only way that pathogenic microorganisms reach the patient. HPV is also transmitted by casual household contact or at the time of birth. In this case, the person carrying the virus may not even know he or she has the infection. A person with a well-functioning immune system is a carrier of the disease, but he himself will not notice unpleasant developments.
In order for the papilloma virus on the labia to begin to manifest itself in the form of proliferation of pathogenic formations, a combination of several factors is required:
- presence of HPV virus in the body;
- reduces the body's protective functions;
- A woman's indifference to her own health.
This virus is not prevented by the patient's immune system and destroys cell division, causing the appearance of benign structures. And if this process is not stopped at the initial stage, protective functions are not restored, then the woman will ask the doctor with a specific question about removing papillomas on the labia, and notright with the question of disease prevention. . The deterioration of immunity, and, accordingly, the activation of viruses, is facilitated by constant stress, seasonal vitamin deficiency, age-related hormonal imbalance or pregnancy.
Note!Men are less likely to have the formation in the genital area, even though they are carriers. The reason for this is also the specific structure of the female genital organs, which is more susceptible to the appearance of small cracks and, as a result, the local protective function is impaired.
Symptoms of papillomas on the labia
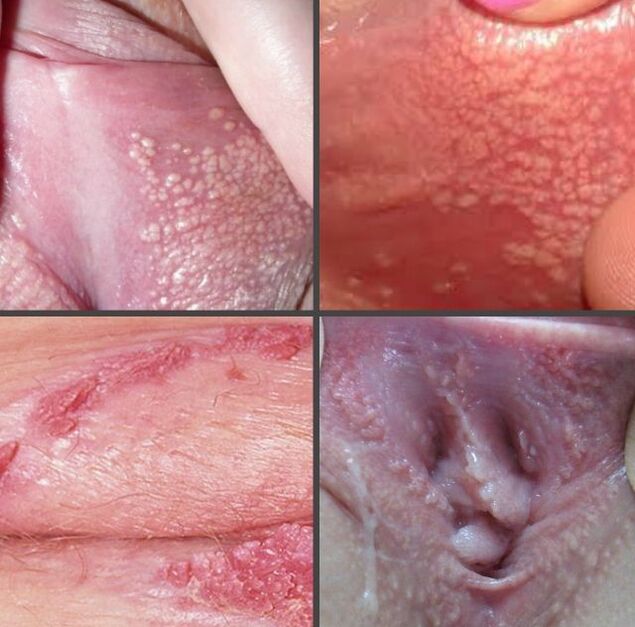
Whatever the cause of infection (violation of hygiene standards in public places or unprotected sex), it is important to determine the presence of the disease in a timely manner. Treatment in the early stages is much easier and faster. To do this, you just need to regularly check your private area yourself as well as visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations.
You can easily find pictures of papillomas on the labia online and compare them with the growing growth. During self-examination or a routine visit to the doctor, the following may be detected:
- Unit formation- small flesh-colored marks, rarely more than 6 mm in diameter.
- Many structures, on the outside these blocks look like a honeycomb. Such growth is evidence of an advanced stage of the disease. If ingredients are damaged during standard cleaning, their color may change from flesh color to dark brown.
Not all structures have a flat shape, some HPV genotypes provoke the formation of masses on thin stems.
Some symptoms that require an immediate visit to the doctor are discomfort and even pain in the private area when performing standard hygiene procedures or having sex and unusual discharge. The labia papilloma virus can initially affect the private parts of the genital area.
Studying photos of labial papillomas yourself and identifying similar appearances does not eliminate the need to see a doctor. Only a thorough diagnosis will help determine the true cause of the disease and determine the best treatment method.
The initial conclusion about papillomas on the labia can be made during a visual examination by a specialist. However, the final diagnosis is made after a series of tests that determine not only the presence of the virus in the body but also the genotype and concentration of active cells. A patient who has not developed a tumor in the genital area but is suspected of having a viral infection will receive a similar list of tests.
List of tests:
- blood and urine to evaluate general health;
- tissue biopsy for established tumors;
- PCR test and Digen test are narrow range tests to confirm the presence of the virus in the body and identify its strain.
The woman should also see a gynecologist, because there is a possibility that viral activity can cause papillomas not only on the external labia, but also on the inside of the reproductive organs (vagina, cervix). Based on the test results and general assessment of the patient's health, treatment is prescribed.
Note!Papillomas on the labia can appear under the simultaneous influence of various strains of viruses, some of which are carcinogenic (16, 18, 33 and others). Only a complete test will help identify all active genotypes.
Treatment methods for papillomas on the labia
A special feature of the treatment of papillomatosis on the labia is its complex nature. That is, the patient is prescribed antiviral and immunostimulant drugs to activate the body's internal reserves to fight the virus (so-called conservative treatment), and if necessary, hardware procedures will be prescribed to remove the tumors. Mild tumors (single and small in size) can also be treated with medications, and in some cases even with compounds recommended by alternative medicine. Therefore, early diagnosis greatly simplifies treatment.
Medicines to treat papillomas on the labia
The main course of internal drug treatment is aimed at improving protective functions. The body is stimulated to fight the virus from within. For this purpose, for papillomas on the labia, the following can be prescribed:
- Antiviral drugs, prevents the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
- immune regulation, thanks to synergistic factors, helps the immune system carry out its tasks.
- immune stimulanthelps the immune system work.
Note!There is no single treatment for labial papillomas. The doctor chooses the drugs, dosage and combination based on the patient's condition, individually in each specific case.
Removal of papillomas on the labia

Many small formations lead to the question of how to remove papillomas on the labia surgically. Modern medicine has many options for hardware procedures to destroy:
- Electric- a rather painful but accessible method that has been proven for many years.
- Cold destruction- removal of formations under the influence of low temperatures.
- Lasers— advanced technology allows you to remove growths painlessly using intense heat.
- Radio knife- the most modern method, removing papillomas in the labia is carried out using directional radio waves.
Traditional surgical interventions today are used extremely rarely if there is a risk of forming a malignant tumor or its large size does not allow removal of the papilloma by another method. Scalpel excision requires a long recovery period and can leave scars afterward.
Note!All of the listed methods can be used to remove papillomas of the external and internal labia. But due to the higher sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the labia minora, a laser or radio knife should be chosen for destruction in this location.
Traditional medicine against papillomas on the labia

When treating papillomas of the labia with folk recipes, you must follow several rules:
- Preparations must be prepared immediately before application to growth, unless this is specifically stated in the formulation;
- Do not exceed the dosage stated in the prescription;
- If at the time of using the product a burning sensation appears, the papilloma begins to grow or deform, you must stop self-medication and consult a doctor;
- If the papilloma does not disappear within the specified time frame, you cannot do without the help of a specialist.
The most popular folk recipes for papillomas of the labia are also the simplest. It is recommended to lubricate the growth with celandine or Kalanchoe juice twice a day. After 2-3 weeks, you can expect the destruction of papillomas.
Another equally popular recipe is compresses made from finely mashed potatoes. Only red potatoes are suitable for treatment. The compress must be replaced with a new one every 12 hours. The procedure is repeated for at least 30 days.
Important!Difficulty in calculating drug concentrations is the reason why most doctors do not support the treatment of papillomas of the labia by traditional medicine. Increasing the dose of the active substance can lead to irritation of neighboring healthy tissues.
Preventive measures for papillomas on the labia
The occurrence of tumors in the genital area is prevented by vaccination against human papillomavirus. Such vaccinations are not mandatory in post-Soviet countries, but can be carried out for adolescents at the request of their parents. Vaccination is recommended for girls between 9 and 15 years old, that is, before they become sexually active.
In addition, preventive measures for papillomas on the labia are:
- comply with personal hygiene rules;
- give up bad habits and promiscuity;
- Proper nutrition and moderate exercise;
- preventive examination by a doctor;
- Refusal to self-treat papillomas in other parts of the body.
The appearance of papillomas on the labia indicates not only the presence of viruses in the body, but also systemic errors (reduced immunity, local inflammation or various diseases). Such signals should never be ignored. It is necessary to remove papillomas on the labia at an early stage, preventing secondary infection or cancerous transformation. Fortunately, modern medicine can remove these pesky growths quickly and almost painlessly.

























